Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Kono, Nobuaki; Shinohara, Nobuo; Sakurai, Takeshi; Nakahara, Yoshinori; Mukaiyama, Takehiko*; Raman, S.*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 144(2), p.129 - 141, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nagaya, Yasunobu; Okumura, Keisuke; Mori, Takamasa
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2002/10
We have analyzed the VENUS-2 MOX core benchmark exercises by using a continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP with the nuclear data set JENDL-3.2 and ENDF/B-VI release 5. The VENUS-2 core is cruciform and consists of three fuel regions; the squared central region, the inner and the outer part of the peripheral region are fueled with 3.3% UO , 4.0% UO
, 4.0% UO and MOX. We have constructed 3-D quarter-symmetric calculation model as precisely as possible. All calculations were performed for 200 million histories including 1 million histories of 50 cycles for the initial guess. The C/E values of keff are 1.00500, 0.99793 for JENDL-3.2 and ENDF/B-VI, respectively. They are in good agreement with the experimental one. However, the JENDL-3.2 result overestimates slightly by about 0.5%. For the pin power distribution, the systematic overestimation can be observed in the MOX fuel region. The calculated results tend to underestimate the measured one slightly in the UO
and MOX. We have constructed 3-D quarter-symmetric calculation model as precisely as possible. All calculations were performed for 200 million histories including 1 million histories of 50 cycles for the initial guess. The C/E values of keff are 1.00500, 0.99793 for JENDL-3.2 and ENDF/B-VI, respectively. They are in good agreement with the experimental one. However, the JENDL-3.2 result overestimates slightly by about 0.5%. For the pin power distribution, the systematic overestimation can be observed in the MOX fuel region. The calculated results tend to underestimate the measured one slightly in the UO fuel regions. However, the dependence on the libraries is not seen.
fuel regions. However, the dependence on the libraries is not seen.
Okumura, Keisuke; Unesaki, Hironobu*; Kitada, Takanori*; Saji, Etsuro*
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2002/10
In order to investigate the calculation accuracy of the nuclear characteristics of LWR next generation fuels, the Research Committee on Reactor Physics organized by Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute has proposed "Reactor Physics Benchmark for LWR Next Generation Fuels". The next generation fuels aim at very high burn-up of about 70GWd/t in PWR or BWR with UO2 or MOX fuels whose fissile enrichments may exceed the Japanese regulatory limitations for the current LWR fuels such as 5wt.% U-235. Twelve organizations have carried out the analyses of the benchmark problems with different codes and data, and their submitted results have been compared. As a result, status of accuracy with the current data and method and some problems to be solved in the future were clarified.
Iijima, Susumu; Ando, Masaki; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2002/10
no abstracts in English
Okuno, Hiroshi; Tonoike, Kotaro; Sakai, Tomohiro*
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2002/10
As the burnup proceeds, reactivity of fuel assemblies for light water reactors decreases by depletion of fissile nuclides, especially in the axially central region. In order to describe the importance of the end regions to the reactivity change, a burnup importance function was introduced as a weighting function to a local burnup variation contributed to a reactivity decrease. The function was applied to the OECD/NEA/BUC Phase II-A model and a simplified Phase II-C model. The application to Phase II-A model clearly showed that burnup importance of the end regions increases as burnup and/or cooling time increases. Comparison of the burnup importance function for different initial enrichments was examined. The application result to the simplified Phase II-C model showed that the burnup importance function was helpful to find the most reactive fuel burnup distribution under the conditions that the average fuel burnup was kept constant and the variations in the fuel burnup were within the maximum and minimum measured values.
Kuroishi, Takeshi; Nomura, Yasushi
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2002/10
To accelerate the slow convergence of the fission source distribution, the matrix k calculation has been developed and incorporated in the ordinary Monte Carlo method. The acceleration can be performed by the fission source correction using the eigenvector of the fission matrix, if the coupling coefficients are approximately evaluated in the middle of Monte Carlo calculation. In this paper, we propose two effective applications of the matrix k, that is, the acceleration repetition method and the source generation method. The former simply repeats the matrix k calculation, and the result for the irradiated fuel pin cell shows enough effective to accelerate the fission source on the criticality estimation. However, in some cases of the loosely coupled multi unit system, the repetition of matrix k more than twice could not be carried out to get into convergence because of many units of low source level. The latter is newly devised here to apply to such cases. The checkerboard fuel storage rack is one of the typical cases, and the calculated results show the effectiveness of this method.
 U,
U,  U and
U and  Pu by using results of in-pile measurements of effective delayed neutron fraction
Pu by using results of in-pile measurements of effective delayed neutron fractionSakurai, Takeshi; Okajima, Shigeaki
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2002/10
The cross section adjustment method was applied to total delayed neutron yields of  U,
U,  U and
U and  Pu of the JENDL-3.2 file by using experimental results of effective delayed neutron fraction
Pu of the JENDL-3.2 file by using experimental results of effective delayed neutron fraction 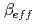 at six cores built in two fast critical facilities of the MASURCA and FCA and a thermal critical facility of the TCA to improve these yields. The adjustment was carried out on the yields given at several incident neutron energy points in the file. Furthermore, to validate these adjusted delayed neutron yields, analyses were performed for the
at six cores built in two fast critical facilities of the MASURCA and FCA and a thermal critical facility of the TCA to improve these yields. The adjustment was carried out on the yields given at several incident neutron energy points in the file. Furthermore, to validate these adjusted delayed neutron yields, analyses were performed for the 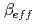 experiments at ZPR fast critical facility. These adjusted yields brought a reduction of uncertainty of calculated
experiments at ZPR fast critical facility. These adjusted yields brought a reduction of uncertainty of calculated 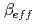 and an improvement in agreement of
and an improvement in agreement of 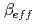 between experiment and calculation.
between experiment and calculation.
Okubo, Tsutomu; Suzuki, Motoe; Iwamura, Takamichi; Takeda, Renzo*; Moriya, Kumiaki*; Kanno, Minoru*
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2002/10
A small scale around 300 MWe reduced-moderation water reactor (RMWR) concept has been developed. For the core, a BWR type core concept with the tight-lattice fuel rod arrangement and the high void fraction is adopted to attain a high conversion ratio over 1.0. The negative void reactivity coefficients are also required, and the very flat short core concept is adopted to make the natural circulation cooling (NC) possible. The core burn-up of 60 GWd/t and the operation cycle of 24 months are also attained. For the system, simplification of the system with the passive safety features is a basic approach to overcome the scale demerit as well as the NC. For example, the HPCF system is replaced with the passive accumulator system resulting in the expensive emergency DGs reduction. The cost evaluation for concerned NSSS components gives about 20% reduction. Since MOX fuels in the RMWR contains Pu around 30 wt% and is irradiated to a high burn-up, the fuel safety evaluation has been performed and the acceptable results have been obtained from the thermal feasibility point of view.
Nakajima, Ken
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2002/10
The nuclear characteristics of TRACY, such as the criticality, the 
 /
/ ratio, the peak power, the energy of pulse, and the total energy, have been evaluated using the experimental data. TRACY is a supercritical reactor fueled with low-enriched uranyl nitrate aqueous solution to simulate criticality accidents in a fuel processing facility, such as a spent-fuel reprocessing plant. In this evaluation, the availability of criticality calculation and the models to evaluate the power and energy have been studied.
ratio, the peak power, the energy of pulse, and the total energy, have been evaluated using the experimental data. TRACY is a supercritical reactor fueled with low-enriched uranyl nitrate aqueous solution to simulate criticality accidents in a fuel processing facility, such as a spent-fuel reprocessing plant. In this evaluation, the availability of criticality calculation and the models to evaluate the power and energy have been studied.
Toshinsky, V.; Hayashi, Hideyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2002/00
None
Oki, Shigeo
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2002/00
None